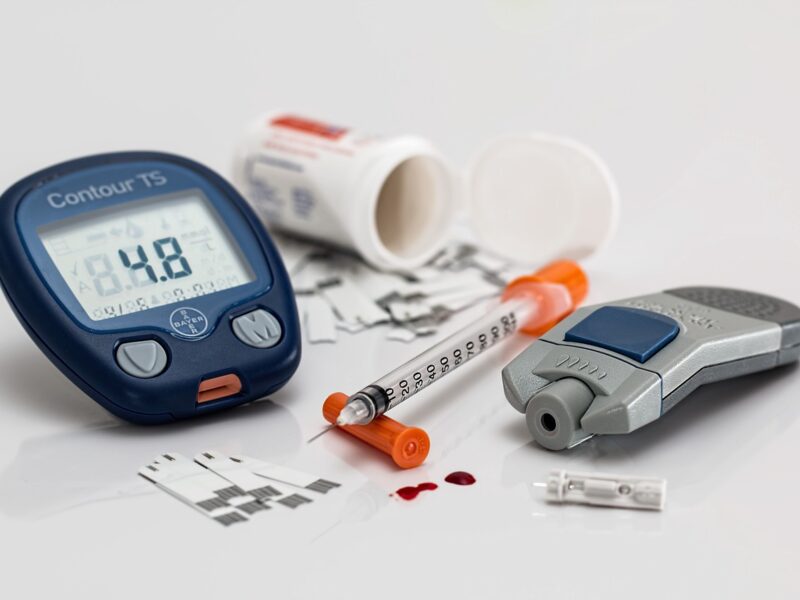
If you have been diagnosed with diabetes by a qualified physician, the next step is figuring out to how to manage your diabetes. To manage your diabetes successfully, you will need to monitor your blood sugar levels judiciously and there are specific equipment used to do this.
Blood sugar monitors, also known as glucose meters, are essential tools for individuals managing diabetes. These devices allow users to measure and track their blood glucose levels, providing critical information for making informed decisions about diet, exercise, medication, and overall health management.
Monitoring blood sugar levels is crucial for individuals with diabetes to maintain their target blood glucose levels, prevent hyperglycemia (high blood sugar) and hypoglycemia (low blood sugar), adjust medications, including insulin. They can reduce the risk of diabetes-related complications such as cardiovascular disease, neuropathy, and retinopathy, and make informed dietary and exercise choices.
Types of Blood Sugar Monitors
There are several types of blood sugar monitors available, each with its unique features and benefits:
- Traditional Blood Glucose Meters: It uses a small drop of blood, usually obtained from a fingertip prick. Blood is applied to a test strip inserted into the meter and the meter provides a reading within seconds. The device is highly accurate and reliable, widely available and relatively inexpensive. It is portable and easy to use.
- Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGMs): it consists of a small sensor inserted under the skin, typically on the abdomen or arm.The sensor measures glucose levels in the interstitial fluid every few minutes and data is transmitted to a receiver or smartphone. The device provides continuous real-time glucose readings, alerts users to high or low blood sugar levels and helps identify trends and patterns in glucose levels.
- Flash Glucose Monitoring Systems: it is similarto CGMs, but do not provide continuous readings.Users also scan a sensor worn on the skin to get a glucose reading. It is less invasive than traditional finger-prick methods and can be more affordable than CGMs.
How to Use a Blood Sugar Monitor
For Traditional Blood Glucose Meters
- Wash Hands: Ensure your hands are clean to avoid contamination.
- Insert Test Strip: Place a test strip into the glucose meter.
- Prepare Lancing Device: Load a lancet into the lancing device and adjust the depth setting.
- Obtain Blood Sample: Prick the side of a fingertip with the lancing device to obtain a small drop of blood.
- Apply Blood to Test Strip: Touch the edge of the test strip to the blood drop.
- Read Result: Wait for the meter to display your blood glucose level.
For Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGMs)
- Insert Sensor: Follow the manufacturer’s instructions to insert the sensor under the skin.
- Attach Transmitter: Connect the transmitter to the sensor.
- Pair with Receiver/Smartphone: Pair the transmitter with the receiver or smartphone app.
- Monitor Glucose Levels: Check the device regularly to monitor glucose levels and receive alerts.
Technological Advancements in Glucose Monitoring
- Smartphone Integration: Modern glucose monitors often come with Bluetooth capabilities, allowing data transfer to smartphone apps. Apps provide detailed graphs, trend analysis, and the ability to share data with healthcare providers.
- Wearable Technology: Wearable glucose monitors, such as CGMs, offer continuous glucose tracking with minimal user intervention.
- Artificial Intelligence and Data Analytics: Advanced algorithms and AI can analyze glucose data to predict trends and suggest personalized interventions. Machine learning models help in improving the accuracy of glucose readings and predicting potential hypo- or hyperglycemic events.
- Non-Invasive Monitoring: Research is ongoing into non-invasive glucose monitoring methods, such as using infrared technology or interstitial fluid measurement without skin penetration.
Blood Sugar Monitor Watches: The Future of Diabetes Management
Blood sugar monitor watches, also known as continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) watches or smart glucose watches, represent a significant advancement in diabetes management technology. These innovative devices combine the functionality of traditional glucose monitors with the convenience and modern features of wearable technology.
How Blood Sugar Monitor Watches Work
Blood sugar monitor watches utilize advanced sensor technology to measure glucose levels continuously. Here’s a breakdown of their operation:
- Sensor Insertion:
- A small sensor is inserted under the skin, typically on the abdomen or arm.
- The sensor measures glucose levels in the interstitial fluid, which is a reliable indicator of blood glucose levels.
- Data Transmission:
- The sensor transmits glucose data wirelessly to the watch.
- Some devices use Bluetooth or other wireless technologies to sync with a smartphone app.
- Real-Time Monitoring:
- The watch displays real-time glucose readings.
- Users can set alerts for high or low blood sugar levels.
- Data Analysis:
- The device tracks trends and patterns in glucose levels over time.
- Users can review their data through the watch interface or a connected smartphone app.
Leading Blood Sugar Monitor Watches
- Dexcom G6: it offers continuous glucose monitoring, customizable alerts, data sharing. It works with smartwatches (Apple Watch, Android Wear) and smartphones, and is highly accurate. It is FDA-approved and no finger-stick calibration is needed.
- Abbott FreeStyle Libre 2: its features includes flash glucose monitoring, real-time alerts, 14-day sensor and compatibility with smartphones and select smartwatches. It is affordable , easy to use, widely available.
- Eversense CGM System: it has long-term sensor (up to 90 days), real-time monitoring, vibratory alerts and can pair with a mobile app for detailed data tracking. Its advantages include long sensor life and on-body vibration alerts for glucose changes.
- Medtronic Guardian Connect: this offers predictive alerts, customizable notifications, real-time data. It syncs with smartphones and notifies users via mobile app, predictive alerts last up to 60 minutes in advance and it offers detailed analytics.
Blood sugar monitors are indispensable tools for individuals managing diabetes, offering vital insights into glucose levels and helping to maintain overall health. With a variety of monitors available, from traditional glucose meters to advanced CGMs, users can choose devices that best suit their needs and lifestyles. Advances in technology continue to improve the accuracy, convenience, and affordability of these devices, empowering individuals with diabetes to take control of their condition and lead healthier lives. Always consult with healthcare providers to select the most appropriate monitoring system and to receive proper training on its use.